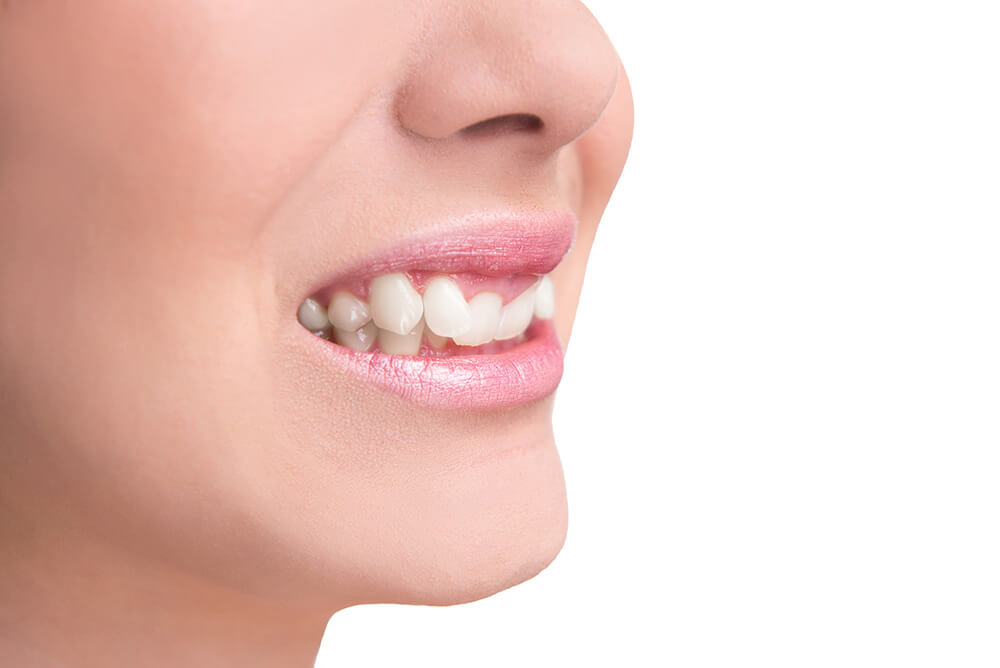
What is an Overbite?
Overbites are identified when the upper teeth protrude over the lower teeth by a proportion of between 30-50%. It is what is medically referred to as a malocclusion. Oftentimes, an overbite can merely appear to be a problem with crooked teeth when in fact the person’s teeth and jaws are not lining up properly. Overbites can often be hereditary, with some people being born with malformed jaws that developed in an uneven manner.
Types of Overbites
Vertical Overbite – Where the top teeth significantly overlap the bottom teeth.
Horizontal Overbite – Occurs when the top teeth protrude over the bottom teeth.
While an overbite is diagnosed as vertical or horizontal, some patients exhibit signs of both types. Overbites can also be categorized as either dental or skeletal in nature. A dental overbite means that the teeth are causing the overbite to be created. A skeletal overbite identifies the jaw as the reason for the overbite to occur.
How is an Overbite Caused?
The most common cause of an overbite is the shape and/or size of the jaw or the teeth. This could mean having too much room in the jaw area or too little room for accommodation of one’s teeth size. If not treated, the overbite will manifest itself into allowing the teeth to crowd each other and grow in crooked if there is too little room, or the teeth will be spaced too far apart if the jaw area is too large. In infants and children, habits like thumb-sucking, sustained and consistent pacifier use and overuse of a bottle, which causes pushing the tongue against the back of the teeth, can produce an overbite. In teens and adults, chronic nail-biting and chewing of writing utensils, such as pencils or other objects, can cause an overbite. So too can losing teeth without timely repair cause an overbite. According to the American Dental Association, nearly 70% of children exhibit the signs of having an overbite.
Other causes for an overbite are:
What Happens If I Don’t Treat It?
If left untreated, an overbite could cause significant health complications. These include irreparable damage to teeth from abnormal positioning and possible jaw pain including temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ).
Other overbite complications include:
- Tooth decay including cavities, gum disease, and worn tooth enamel
- Jaw pain
- Severe headaches
- Discomfort or pain while eating
- Trouble with fully opening or closing mouth
- Sleep apnea
- Difficulty speaking
An untreated overbite could also dramatically alter the facial structure and lead to psychological issues like low self-esteem. If the causes of the overbite have begun in early childhood and are continuous and severe enough, the aesthetic deterioration will take place as early as pre-pubescence and may lead to bullying issues by peers.
Treating an Overbite and Correcting It
Generally, a dentist will refer a patient with an overbite to an orthodontist for treatment. In children, they are easier to treat because a child’s jaw is still in the developmental stages. For children and teens, the most common issue is crowding of teeth in the mouth. For many adults with an overbite problem, the lack of preventative treatment early in life has led to the more severe symptoms associated with overbites. In either case, the orthodontist or dentist will examine the area and write up a treatment plan that can last for up to two years and possibly longer. Initial x-rays will be taken to determine the type of overbite and the relationship between the teeth and the jaw in determining the best treatment.
Here are some treatments your orthodontist may recommend to correct an overbite issue:
Children and Teens
- Removal of baby teeth (making room for permanent teeth to grow in straight)
- Growth modification device (used best during growth spurts) – helps to better position the jaw
- Braces – slowly moves the teeth to correct the overbite as well as the jaw
- Retainers – device used post-braces that help to keep the teeth in place
Adults
- Braces – move only the teeth to correct an overbite
- Teeth removal – dentists and orthodontists try to avoid this procedure but will do this in very severe overbite cases to allow the teeth more freedom to move.
- Surgery – jaw problems for skeletal-type overbites can only be corrected with surgery for adults.
If your overbite is causing issues, it’s important to make an appointment with your orthodontist or oral surgeon for treatment. In all cases, whether child or adult the best way to prevent dental issues from occurring is to make sure you visit a dentist early and often. They recommend a checkup for children by at least the age of 7 for the detection of an overbite. Adults need to get regular checkups every six to twelve months to ensure early intervention to avoid the potentially severe physical repercussions of leaving an overbite untreated. Absolute Dental has orthodontists in Reno, Las Vegas, and Carson City, NV. Schedule an appointment today to discuss potential treatment options that may be suitable for you or your loved one.